Alkenes are hydrocarbons are formed only of Carbon and Hydrogen. They are contain a double carbon (C=C) and are often known as unsaturated molecules (for information on saturated molecules visit the alkanes page)
Synthesis
Alkenes can be synthesised using two methods
- Cracking of alkanes
- Dehydration of alcohols
Reactions
Alkenes undergo many different reactions.
- Addition
- Hydrogenation
Addition of hydrogen across the double bond - Halogenation
Addition of halogens across the double bond - Hydration
Addition of water across the double bond
- Hydrogenation
- Polymerisation
- Opening of the double bond to form a large molecule known as a polymer.
Addition
Hydrogenation

Hydrogenation of ethene to form ethane.
C2H4 + H2 -> C2H6
Halogenation
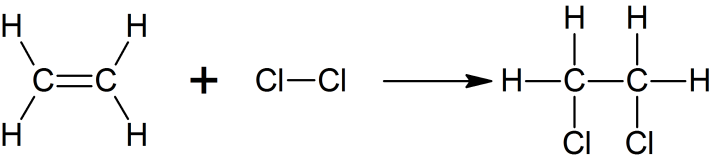
Halogenation of ethene to form 1, 2-dichloroethane
C2H4 + Cl2 -> C2H4Cl2
Hydration

Hydration of ethene to form ethanol
C2H4 + H2O -> C2H5OH

You must be logged in to post a comment.